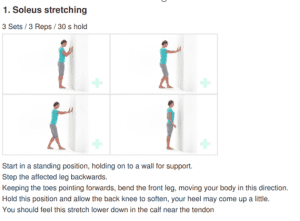
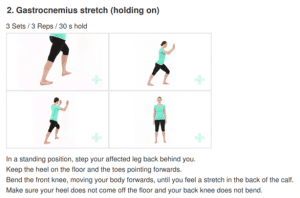
Medial Elbow Pain Explained
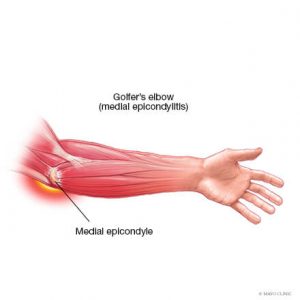
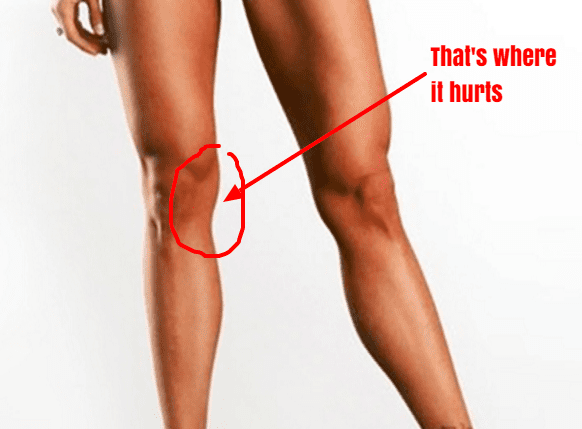
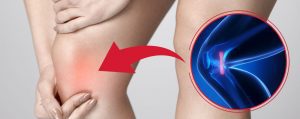
Medial elbow pain is also known as medial epicondylitis or golfer’s elbow. It is typically associated with pain on the inside (medial side) of your elbow and can spread into your forearm and wrist. This pain is the result of overloading and damage to the tendons that flex your wrist towards your palm.
Causes
This condition is triggered by damage to tendons and muscles which control your fingers and wrist. This damage is associated with excessive or repeated stresses- particularly repetitive and forceful finger and wrist movements, incorrect lifting, hitting and throwing techniques, lack of warmups and/or poor muscle conditioning.
Key risk factors for developing medial elbow pain may include smoking, obesity, being of in age bracket of 40 years old and over and undertaking repetitive activity with your arms for at least two hours daily. High risk occupations may include chefs, office desk workers, plumbers, construction workers, painters, butchers and assembly line workers. Those who partake in sports such as golf, racket sports, rowing, weight lifting and baseball are also at a higher risk.
Symptoms
Symptoms may be triggered suddenly due to a traumatic incident or may gradually develop over time and include but are not limited to:
- Tenderness and pain is typically felt on the inner side of your elbow (particularly on the bony knob), and may refer along the inner side of your forearm and down to your wrist and fingers. It often worsens with certain movements. For example, bending your wrist towards your palm against resistance, or when squeezing a rubber ball.
- You may feel stiffness in your elbow, and making a fist may hurt
- You may experience weakness in your forearm, wrist and hand
- You may experience tingling and numbness that can radiate into one or more fingers — typically to your ring and little fingers.
Diagnosis
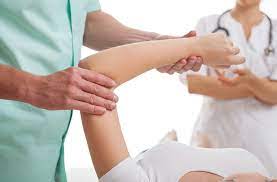
This condition is typically diagnosed based on your medical and occupation history and a physical exam by your doctor or physiotherapist. To evaluate stiffness, strength and pain, your clinician may apply pressure to the impacted region and get you to move your elbow, wrist and fingers in various ways. You may also be referred on for imaging such as X-rays and Ultrasounds to aid diagnosis.
Management
A mix of non-surgical treatment options are effective for the majority of medial elbow pain cases, and self-resolves over time. You should rest your elbow and painful activities should be avoided. But it is very vital to maintain gentle movements of the forearm, elbow, and wrist through its range of motion.
Potential treatment options include:
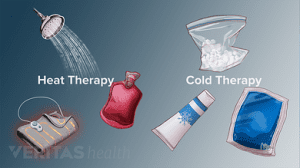
- Ice
- Rest
- Physiotherapy and acupuncture
- Anti-inflammatory medications as recommended by your doctor or pharmacist
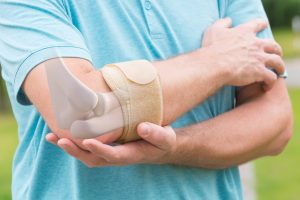
- The use of a wrist and forearm brace or splint to support and rest your forearm
As your initial elbow pain lessens, your muscles around the elbow, forearm and wrist should be safely strengthened and stretched under guidance of a physiotherapist. Your physiotherapist will advise you on particular exercises, give you appropriate symptom management advice and take you through a personalised graduated rehabilitation program. If you continue to experience pain after 6-8 weeks of treatment, your physiotherapist can refer you back to your doctors, to consider administration of a cortisone injection into the elbow to help reduce pain and inflammation, and further referral onto see a specialist to seek guidance on other treatment options.
Prevention
Having a good comprehension of risk of injury and being conscious of your everyday activities may aid in the prevention of medial elbow pain. You should:
- Adopt appropriate technique and form when undertaking repetitive activities or sporting motions
- Keep up with adequate wrist, forearm, and shoulder muscle strength
- Undertake gentle wrist and forearm stretches pre and post activities
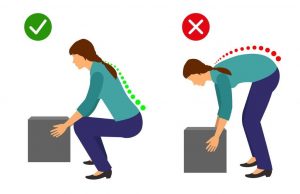
- Adopt appropriate posture and body mechanics when lifting heavy objects to reduce joint strain- especially if doing so repetitively