Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) Explained
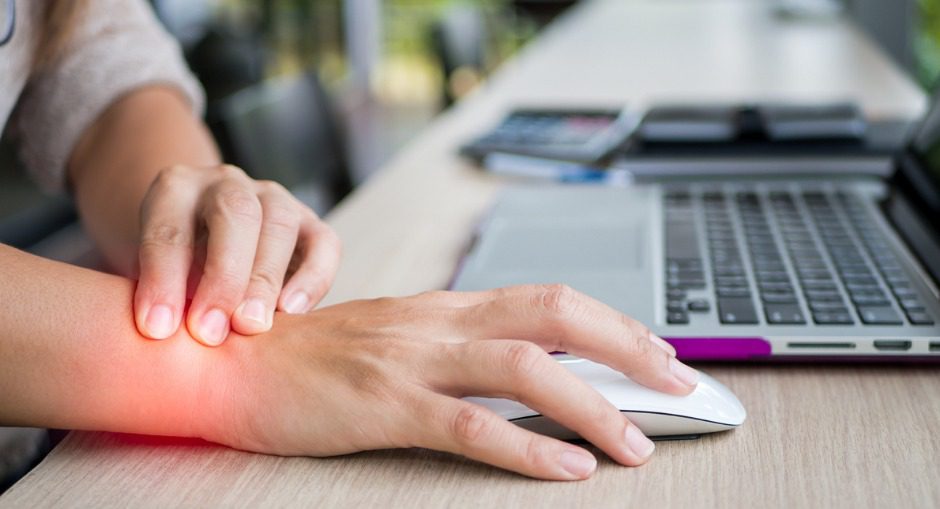
RSI is typically defined as an overuse disorder- a gradual build-up of overload to nerves, tendons, and muscles arising from repetitive movements or activities. Repetitive use of the same motions leads to inflammation and damage to these soft tissues. This disorder mostly affects the upper limb- particularly the elbows, hands and wrists.
Causes
Possible causes of RSI include but are not limited to:
- Undertaking the same and repetitive movements and stressing the same muscle groups
- Working in cold environments
- Assuming a sustained and/or awkward posture for prolonged periods of time
- Undertaking a particular activity for prolonged periods of time with no rest-breaks
- Frequent and prolonged use of vibrating equipment
- Adopting poor postures from working at inappropriately designed workstations
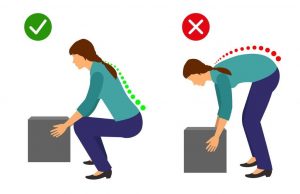
- Undertaking a motion which involves carrying and/or lifting heavy items
Symptoms
RSI leads to a gradual development of a broad variety of symptoms, which range from mild to severe in severity. RSI particularly affects the muscles and joints of your wrists, hands, elbows, forearms, shoulders, neck. Having said this, RSI can affect other areas of the body as well.
Common symptoms may include:
- Pain
- Tingling
- Cramping
- Increased sensitivity to heat and cold
- Tenderness
- Fatigue
- Loss of strength
- Throbbing
- Soreness
- Achiness
- Stiffness
- Struggling with typical activities of daily living, such as gripping and twisting motions, carrying light weights, writing, kitchen prepping, dressing, personal cares etc
You may develop these symptoms when you undertake a task repetitively for a period of time, and can settle when you stop. Symptoms may settle over a few hours or over the course of a few days. However, if left untreated or is poorly managed, a minor RSI may gradually progress to a nasty chronic injury.
Diagnosis
If you experience mild discomfort whilst completing particular activities at home or at your job, it is a good idea to see your GP or physiotherapist to talk about RSI. But an RSI is not always simple to diagnose as there is no particular clinical test for it. Your GP will enquire about your medical history, occupation and work environment, and other activities to attempt to identify any repetitive motions you undertake that may be the cause of your symptoms. A physical examination will be undertaken, where they will assess your movement, check for pain, inflammation, sensation, tenderness, strength and reflexes in the impacted body part. RSI may be triggered by specific health disorders like bursitis, carpal tunnel, tigger finger, ganglion cyst, or tendonitis (inflammation in your tendons). Your GP can refer you on further diagnostic tests such as X-rays, Ultrasounds, blood tests, MRIs, nerve conduction tests etc, to determine if these underlying disorders may be the cause of your symptoms. You may be also be referred onto a physiotherapist and acupuncturist for conservative treatment and management for mild-moderate issues. If symptoms persist, you will then be referred onto a specialist.
Management
Initial treatment options for the management of RSI symptoms is conservative. This includes:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE principles)
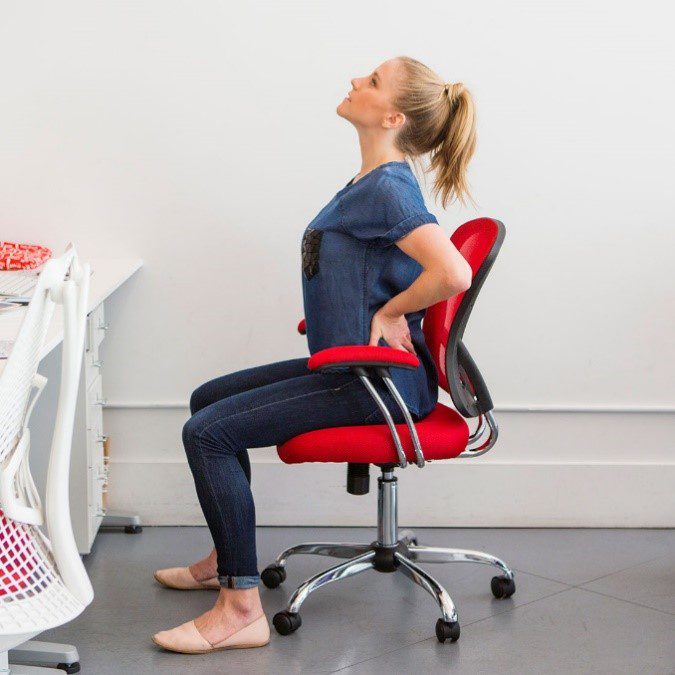
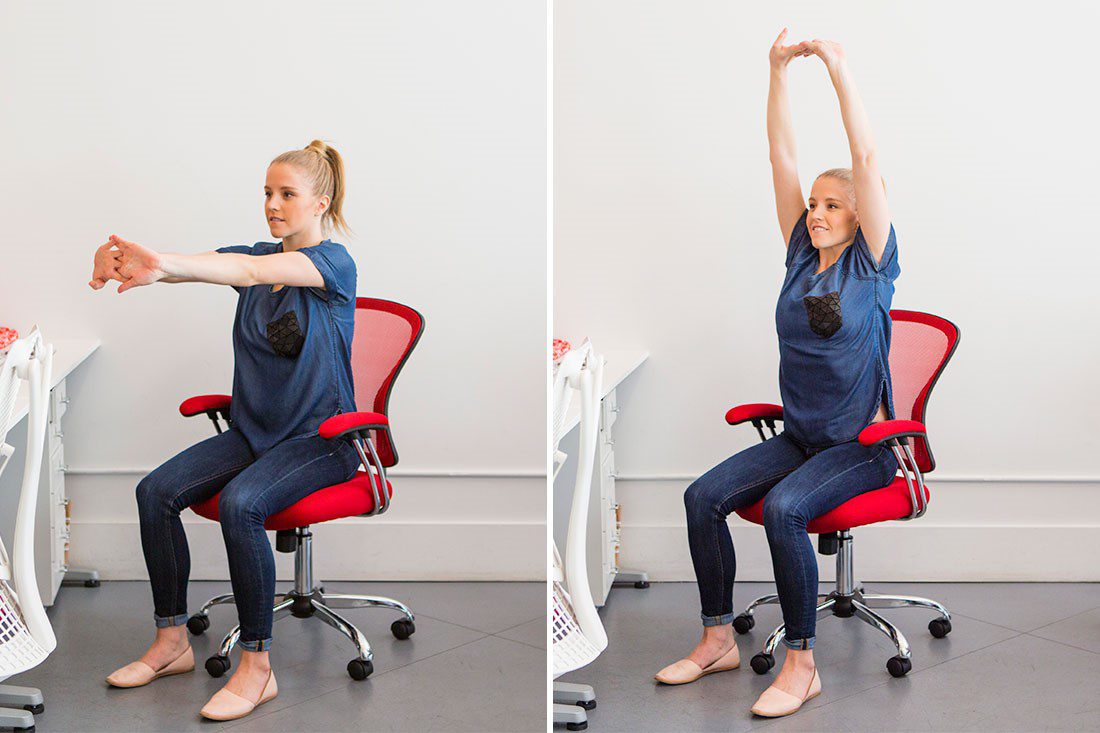
- Taking regular breaks between tasks and looking after your posture
- Undertaking your activities and movements with appropriate form and posture
- Intake of Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), both oral and topical as prescribed by the GP
- Use of cold and heat to the impacted area
- Administration of steroid injections into inflamed joints and tendons
- Tailored exercise prescription from physiotherapists to correct posture and strengthen and stretch affected muscles
- Acupuncture
- Stress reduction and relaxation training
- Use of splints and braces to help protect and rest the affected muscles and tendons
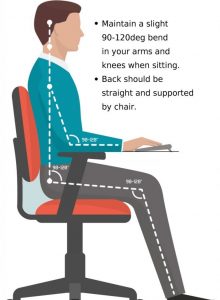
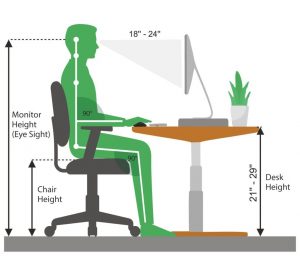
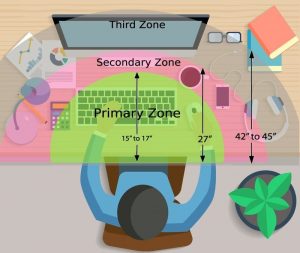
Ergonomically appropriate adjustments to your workstation and work environment may be recommended by your physio and GP- for example resetting your desk and chair if you’re working at computer, and alterations to your equipment and activities/motions to lessen the strain and stress on your muscles and joints. Surgery may be necessary in some cases.
Prevention
Minimizing repetitive actions particularly if they involve the use of heavy machinery or vibration. Improving your working posture and work-environment as well a taking regular breaks. Employers often undertake risk-assessments when you join a company to determine that the work area is ergonomically fit, comfortable and appropriate for you. You may be able to request for an assessment if you have not had one or are having issues with your work environment