Osteoporosis
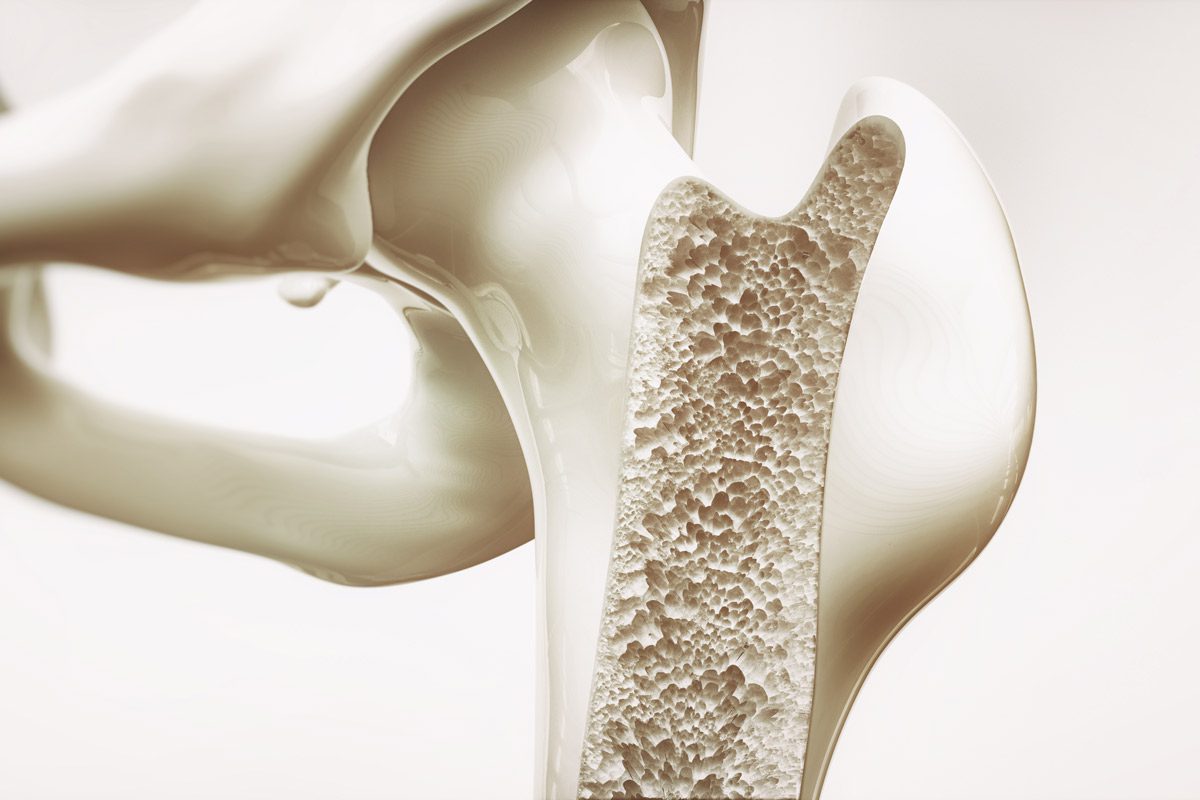
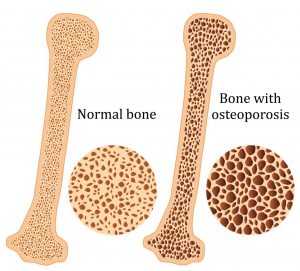
Osteoporosis is a condition which results in weak and brittle bones- to such degree that a fall or even mild stresses like coughing or bending over may result in a fracture. Bones are living tissues which are continually being broken down and replaced. However, your bones become osteoporotic when the formation of new bone does not keep up with the loss of old bone. This condition typically develops over time without any pain or other major symptoms, and is generally not diagnosed until you have sustained a fracture. The hip, pelvis, upper arm, spine and wrists are the most common structures affected by osteoporosis- related fractures.
How do you know if you have Osteoporosis?
Because there are no obvious early warning signs and symptoms, it is difficult to pre-diagnose osteoporosis. You may be unaware that you have this condition perhaps till you have one of the following:
- Sustained a fracture from an incident more easily than you should have- like a simple fall or a bump
- A decrease in the height of your spinal vertebrae over time
- Change in posture – stooping or bending forwards
- Back pain, due to a fractured or collapsed vertebra
Please see your doctor if you experience the following:
- If you are over the age of 50 and have sustained a fracture
- Sustained a spine, wrist, or hip for the first time
- Sustained a fracture more easily than you should have (a simple fall or after a slight bump)
Risk factors
Key factors which may increase your risk of developing osteoporosis include:
- Females- particularly post-menopausal Caucasian and Asian women
- Over the age of 50
- Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol
- Smoking
- Having a smaller or petite body frame
- Poor physical activity levels and leading a very sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Having low levels of vitamin D and poor dietary calcium intake
- Decreasing levels of testosterone with ageing in men
- Estrogen deficiency in women (irregular periods, early (before turning 40) or post-menopausal, surgical removal of the ovaries)
- Use of long-term medication such as thyroid and epilepsy medications, corticosteroids
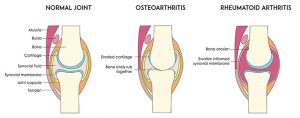
- Having medical conditions such as gastrointestinal diseases; endocrine diseases; rheumatoid arthritis; cancer; and blood disorders
How will you be diagnosed?
Your doctor will review your signs and symptoms, family and medical history. You may be referred on for a specialized X-ray or CT scan to evaluate the bone density to help diagnose osteoporosis. Your bone density will be classified by comparing it to the typical bone density for a person of equivalent gender, size, and age.
How is Osteoporosis treated?
The treatment pathway chosen for the management of this condition is dependent on results of your bone density scan, gender, age, medical history and severity of the condition. Potential treatments for osteoporosis may include exercise, making positive lifestyle changes, vitamin and mineral supplements, and medications. Please consult your doctor for appropriate advice and treatment options.
How can Physiotherapy help?
Your physiotherapist will help you strengthen your bones and your muscles through a personalized and graduated rehabilitation program. Components of this rehabilitation program may include weightbearing aerobic exercises, resistance training using free weights/resistance bands/bodyweight resistance, and exercises to enhance posture, balance and body strength. Your physiotherapist will work with you to find activities that suit your needs and as per your physical activity level.