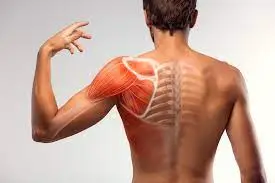
What is your Rotator Cuff and What does it do?
You may have seen videos or posts online about people talking about a specific area of your shoulder known commonly as the “Rotator Cuff” and wondered what they were on about. Your shoulders do a lot of important things you might take for granted! They help you get something off a high shelf, comb your hair, or play a game of cricket.
It’s a complicated process that your body makes look easy. And your rotator cuff is a big part of that. It protects and stabilizes your shoulder joint and lets you move your arms over your head. It’s importance is widely used in sports like swimming, tennis and netball.
In New Zealand healthcare, shoulder injuries have one of the highest prevalence when it comes to ACC claims and overall cost. Within this, rotator cuff injuries are among the most common pathologies affecting New Zealanders. Other pathologies include acromioclavicular injuries, dislocations, osteoarthritis and frozen shoulder.
So, what exactly is the cuff and how does it influence the shoulder?
-
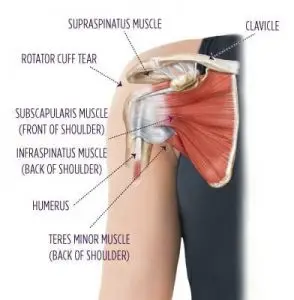
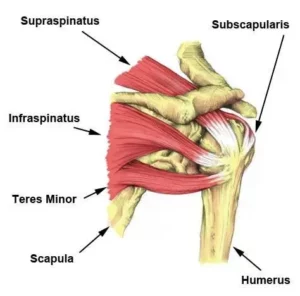
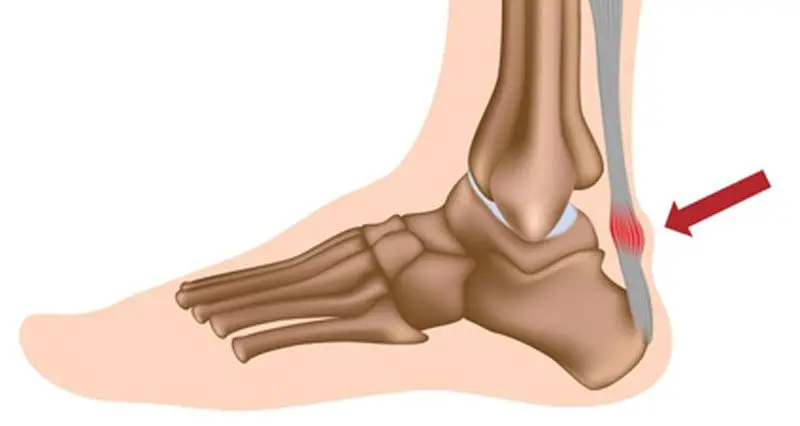
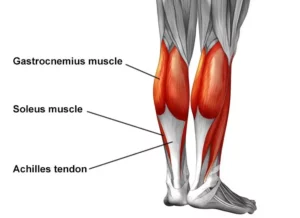
The rotator cuff (RC) is a combination of four muscles that run through and attach onto specific areas of the humeral head (top of the arm bone).
-
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor and Subscapularis are the four muscles comprising the RC and each one plays an important role however they all contribute to shoulder stability:
|
A thin triangular muscle that helps perform abduction |
A thicker, triangular muscle that performs external rotation. |
The smallest muscle of the cuff, helps with rotation as well |
The largest muscle of the cuff performs internal rotation (arm behind your back!) |
Many people suffer from shoulder pain, so here are the most common injuries that can happen at the rotator cuff:
Rotator Cuff Tear:
A rotator cuff tear is often the result of high levels of load over a short amount of time or a high impact force stressing one or more of the tendons/muscles. Fortunately, majority of tears are partial. Tears are more common in people with jobs that involve heavy loading or lifting or in high impact sports like rugby. It also can happen suddenly if you fall on your arm or try to lift something heavy. Common and easily treatable with conservative management by a physiotherapist, a rotator cuff tear can come right.
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy:
A rotator cuff tendinopathy is the most common shoulder pain complaint/injury resulting in inflammation and irritation of one or more of the cuff tendons. This pathology is more common in individuals who have an occupation where repetitive use of the shoulder, particularly in an overhead position such as carpenters or painters, or individuals that play highly repetitive, throwing sports like tennis, baseball or volleyball. Once again, this injury is treatable by a physiotherapist, conservative management can be very effective in treating these injuries with a thorough, well planned exercise program to help get patients back to doing what they love.
Majority of people experience pain around the shoulder joint, with some movements being highly provocative. Tenderness on touch at the affected site is also common – this helps your physiotherapist hone in on potentially which tendon is causing those problems!
Medical management vs Physio management
Medical management will be advised by your local GP if you decide to see them first. They might prescribe NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen) to help with the pain you’re experiencing and recommend you see a physiotherapist. Depending on your injury as well as your ability to function, surgery may be an option if conservative medical and physio treatments don’t help. Most people get by without the need of surgery but some tears can be too large to heal without the use of surgical intervention.
Physiotherapy management is designed around reducing pain and disability, restoring range of motion and helping people return to work or sports to perform how they were prior to the injury. In the early stages of these injuries, rest and ice and/or heat are recommended to allow the inflammation to settle – then your physiotherapist will begin to introduce a detailed exercise program, this may include:
- Isometric (static hold) exercises
- Resisted movements using bands
- Range of motion exercises to restore lost movement
- Functional loading – task specific or sport specific
If this is successful, the last step is to build back up the strength that was lost over time – this is done by concentrically (against gravity) loading the affected tendons/muscles in a way that they adapt and lay down more tissue, grow and becoming stronger in hopes that you get to return to what you enjoy!