Wrist pain: De Quervains tenosynovitis
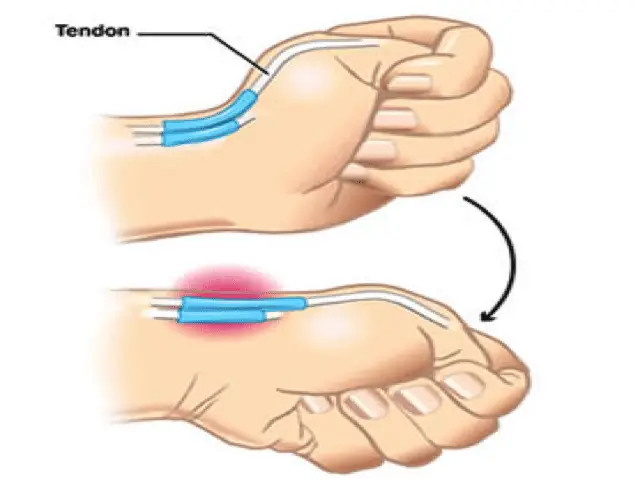
De Quervains tenosynovitis is a painful condition caused by inflammation of two prominent tendons that are located at the wrist and thumb.
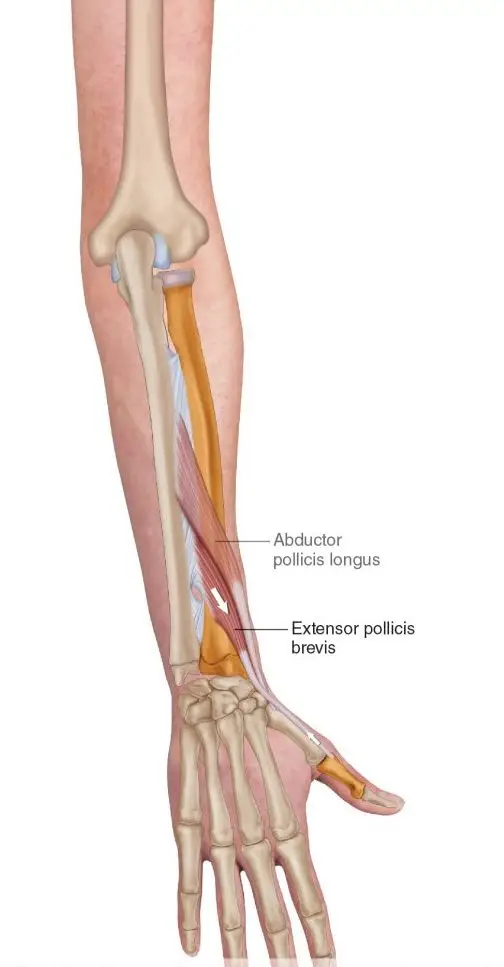
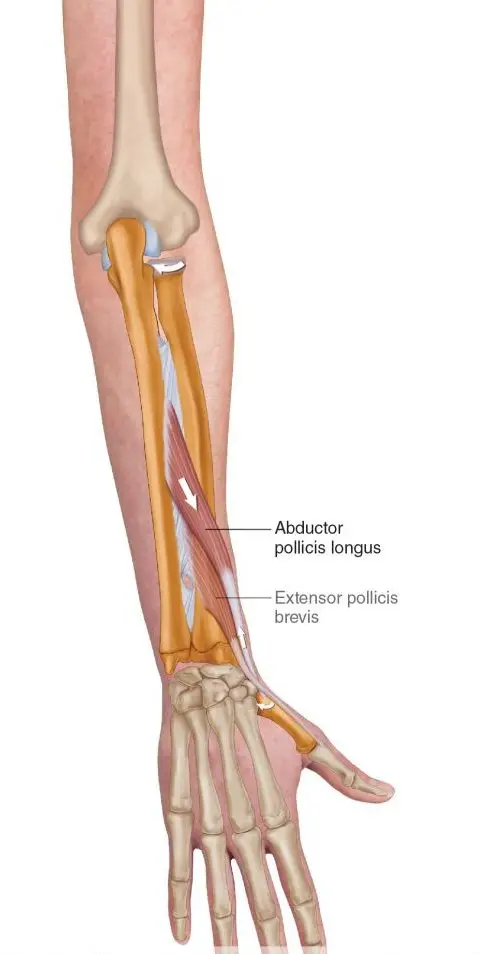
The two tendons called the Extensor pollicus brevis and Abductor pollicus longus originate from the middle of the forearm travel down towards and over the wrist to insert into the thumb. Collectively they function to extend the thumb, whilst abductor pollicus longus extends and also abducts the thumb (lifting thumb up to the ceiling).
What causes it?
The most common cause of De Quervains tenosynovitis is the repetitive overuse of thumb and wrist whether it is occupational or hobby related. For example, the repetitive thumb movement whilst using scissors by hair dressers, landscapers using shears or whilst gardening). Trauma to the tendons from injuries to the wrist or the thumb can cause inflammation of the tendons.
In some cases, age related degeneration of the tendon sheath or underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of the developing De Quervains tenosynovitis. Hormonal changes resulting in fluid build up in young mothers can commonly result in De Quervains tenosynovitis.
Symptoms
Commonly your symptoms may include:
- Pain located at base of your thumb
- Pain elicited by movement of thumb (gripping or making a fist)
- Grating or snapping feeling
- Tightness in the wrist
- Swelling surrounding the base of thumb and wrist
How is De Quervains tenosynovitis diagnosed?
Your doctor or physiotherapist will be able to diagnose the condition based on your symptoms and after doing a thorough movement assessment to rule out any other potential diagnosis.
- Finkelstein test is used to elicit symptoms to confirm De Quervains tenosynovitis.
How to test:
- Wrap your thumb with your fingers.
- Slowly bend your wrist down
A positive test would elicit pain at the site of the two tendons.
Radiological investigations in lights of ultrasound and an x-ray might be recommended for further investigations, particularly to confirm clinical diagnosis or to rule out any other possible causes of De Quervains such as osteoarthritis.
What treatment options are available?
Conservative (non-surgical) management
Conservative management measures are generally recommended as the first line of management for mild to moderate symptoms. This is because up to 60-70% of symptoms are likely to improve over a period of 6-8 weeks of regular physiotherapy intervention. In this period, the following strategies are recommended by your therapist to fast-track your recovery
- Rest and application of heat or cold packs
- Avoid repetitive use of thumb
- Pain medications (anti-inflammatory medications) such as diclofenac or ibuprofen
- Splints or braces
- Steroid injection
Surgical management
In more severe cases when conservative management has failed, surgery may be recommended by an orthopaedic specialist or surgeon.
Prior to your surgery you will have the opportunity to thoroughly discuss with your surgeon the details of the surgical procedure and about the post operative rehabilitation process.
-
Surgical procedure
Surgery may be performed under general or local anaesthesia. A small incision is made at the wrist and thumb region. The covering of the tendons (sheath) is then separated and expanded to provide the tendon space to allow the tendon to move smoothly within the sheath. After this the, the incision in then sutured with a firm dressing applied over the suture site.
- While you recover from the surgery, an information sheet with post operative guidelines will be provided to you by your surgical team. It is important that you must follow the guidelines recommended by your surgeon for optimal recovery.
- In most cases your will have a follow up with your surgeon few weeks after your surgery to check your wound healing and your progress. You are often times referred to physiotherapy for strength and conditioning of your wrist and hand movements to facilitate your recovery.