Ankle injuries – Your first step to recovery
Common? Oh Yes!
The road to recovery
Investigations
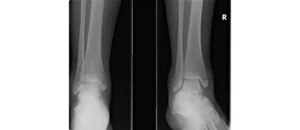
In some cases, initial X – rays are done to rule out broken bones.
Ultrasounds can be used to diagnose some ligament and tendon damage.
MRI is the best form of imaging but this does come at a higher cost and higher exposure to radiation. These are usually done after failed conservative treatment or in instances where pain remains high for longer periods.
A CT scan is helpful with complicated foot and ankle fractures. It will normally be ordered by a specialist surgeon who is planning for an operation.
What to look out for
Ankle sprains:
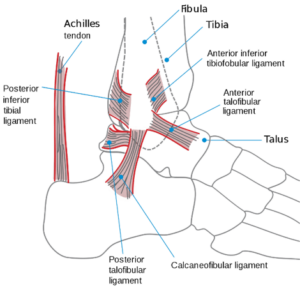
This is normally a twisting injury that causes a stretch or tear of ligaments surrounding the ankle. Your health care professional will provide you with all the information and tools you need for recovery.
These heal relatively quickly when the outside border of the foot is affected and a little slower when the inside border of the ankle is affected.
You will normally feel pain on certain ankle movements, stiffness in the ankle and experience some swelling and bruising.
Ankle Fractures:
These normally present with swelling, bruising and pain initially – although not always. In some cases, it is too painful to put weight on the ankle.
They are usually best confirmed with X – ray and specialist referral.
Management may be surgical or non-surgical depending on the severity and site of the fracture.
Fractures generally take longer to recover compared to sprains.
What treatment to expect
Acute phase:
Your healthcare professional will normally initiate techniques to minimise your pain and swelling with rest, ice, compression and elevation.
Analgesia and anti – inflammatory medication may also be used.
Strapping may be used for stability at this stage and can be done by your physiotherapist.
You will also be encouraged to increase movement and begin strengthening.
Rehabilitation phase:
Balance and proprioceptive exercises will be given to you by your physiotherapist.
Strengthening will continue and running will start soon.
Once running in a linear motion pain free, you will progress to sport specific exercises.
Finally, you will return to sport or previous function such as trekking with a graded program.
Strapping may continue for up to 12 months after your injury in order to prevent re – injury.
What can you do on the day of the injury?
Rest by reducing time spent walking or standing. This will help the ankle to heal.
Ice the ankle for up to 20 minutes every couple of hours.
Compress the ankle with a firm bandage during the day and remove the bandage at night.
Elevate the leg.
Attempt circulatory exercises such as ankle circles and foot pumps (About 10 – 30 repetitions every couple of hours).
Contact your health professional or physiotherapist in order to make appointment for assessment.
If you are unable to stand on your leg or have excruciating pain in the ankle, head on to the local emergency department for immediate investigation.